UB Tools with Natrolite Data#
This tutorial demonstrates how to use the UB tools in NeuXtalViz to process CORELLI Natrolite data (chemical formula \(\mathrm{Na_2Al_2Si_3O_{10}\cdot 2H_2O}\)).
Step 1: Convert to Q#
In the Convert to Q tab:
Set the instrument to CORELLI.
Enter the IPTS and run numbers for the Natrolite dataset.
Set the wavelength range and select the appropriate calibration file.
Click Convert to Q to load the data and build the Q volume.
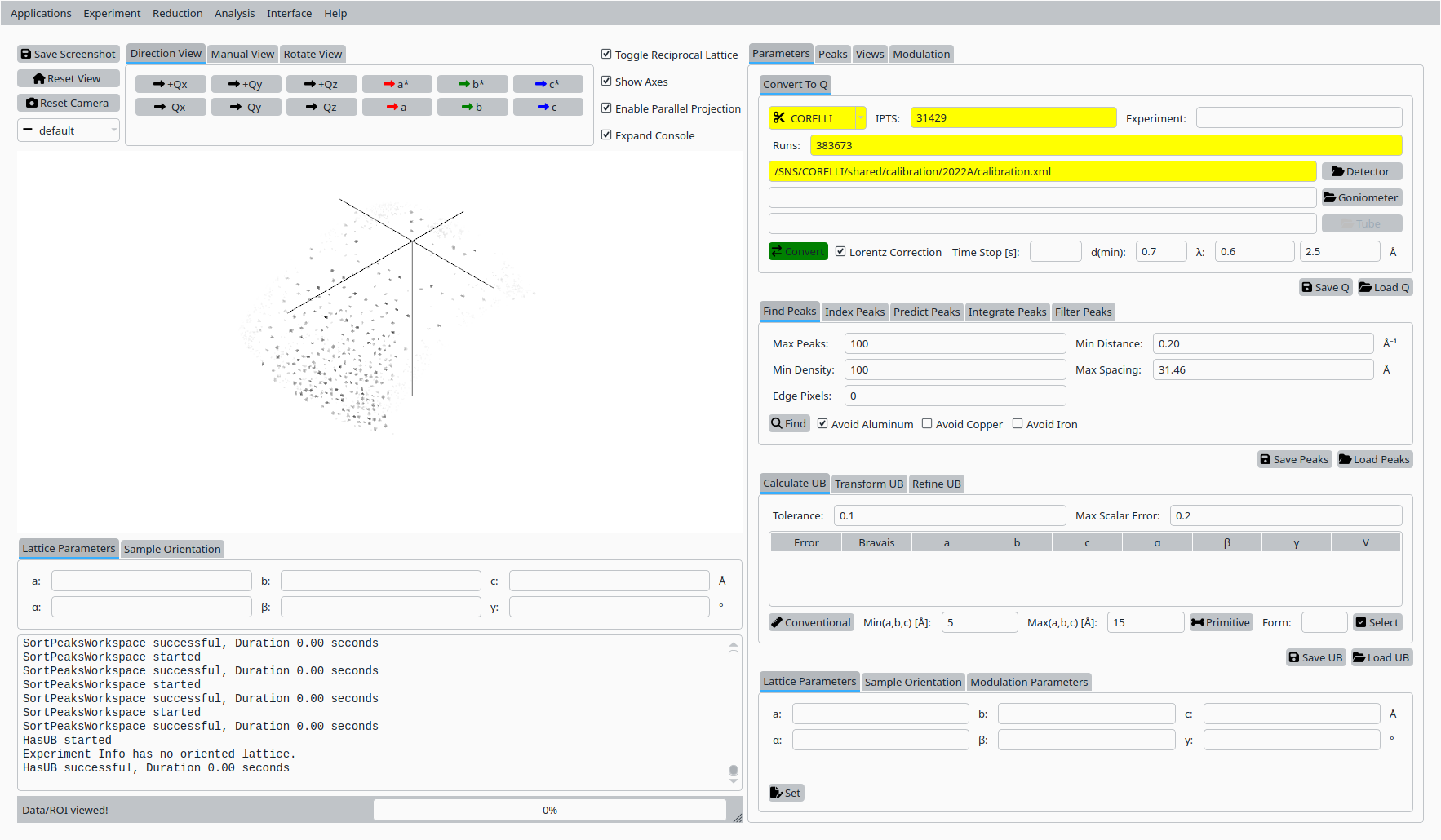
Convert Natrolite data to Q for CORELLI.#
Step 2: Add reference peaks#
In the Inspect / Verify tab:
Use the horizontal, vertical, and diffraction controls to define a region of interest in the detector view.
Set the coordinates for the first reference reflection and click Add Peak to record it.
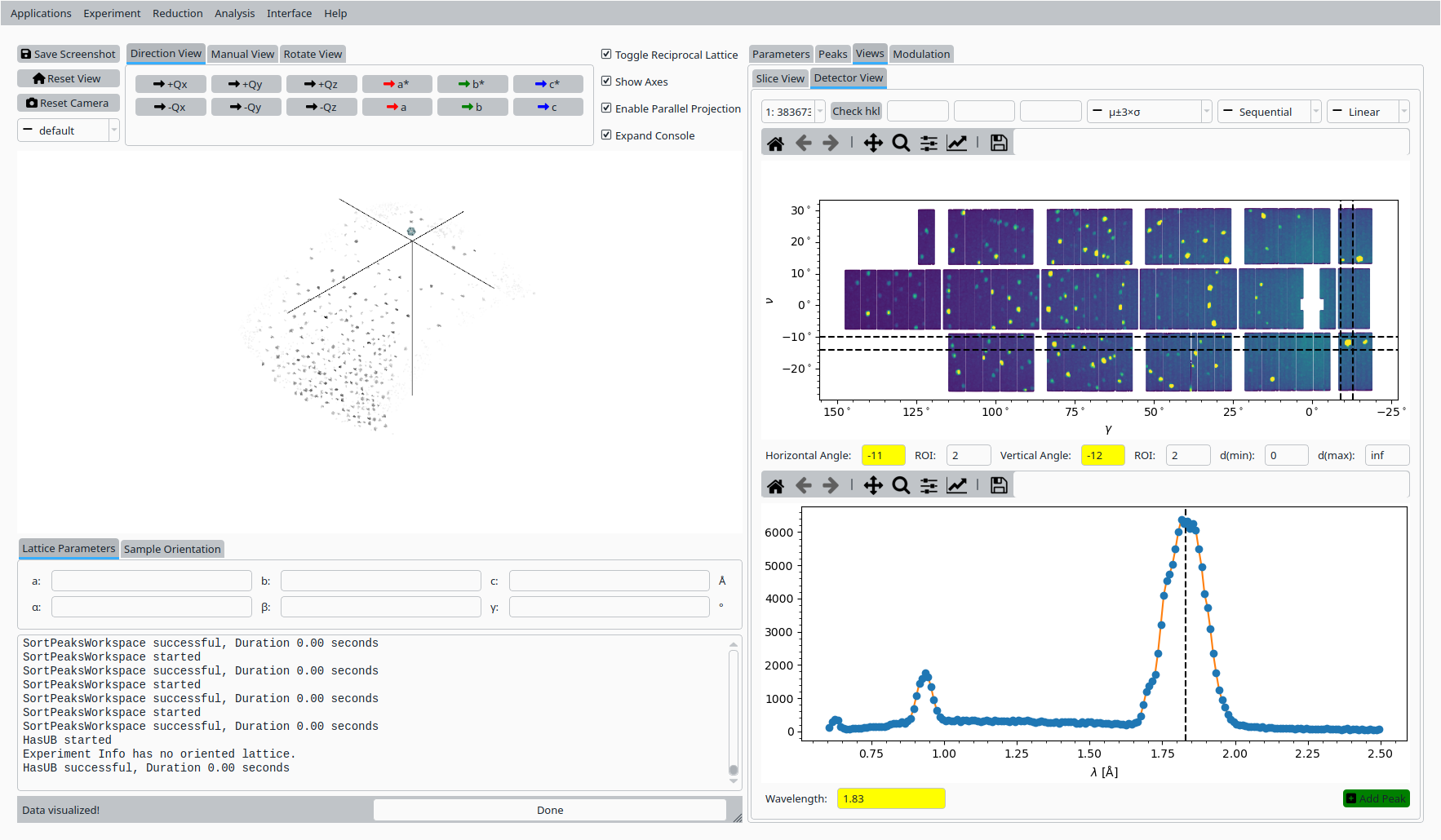
First reference peak for Natrolite on CORELLI.#
Adjust the ROI and diffraction coordinate for a second reflection and click Add Peak again.
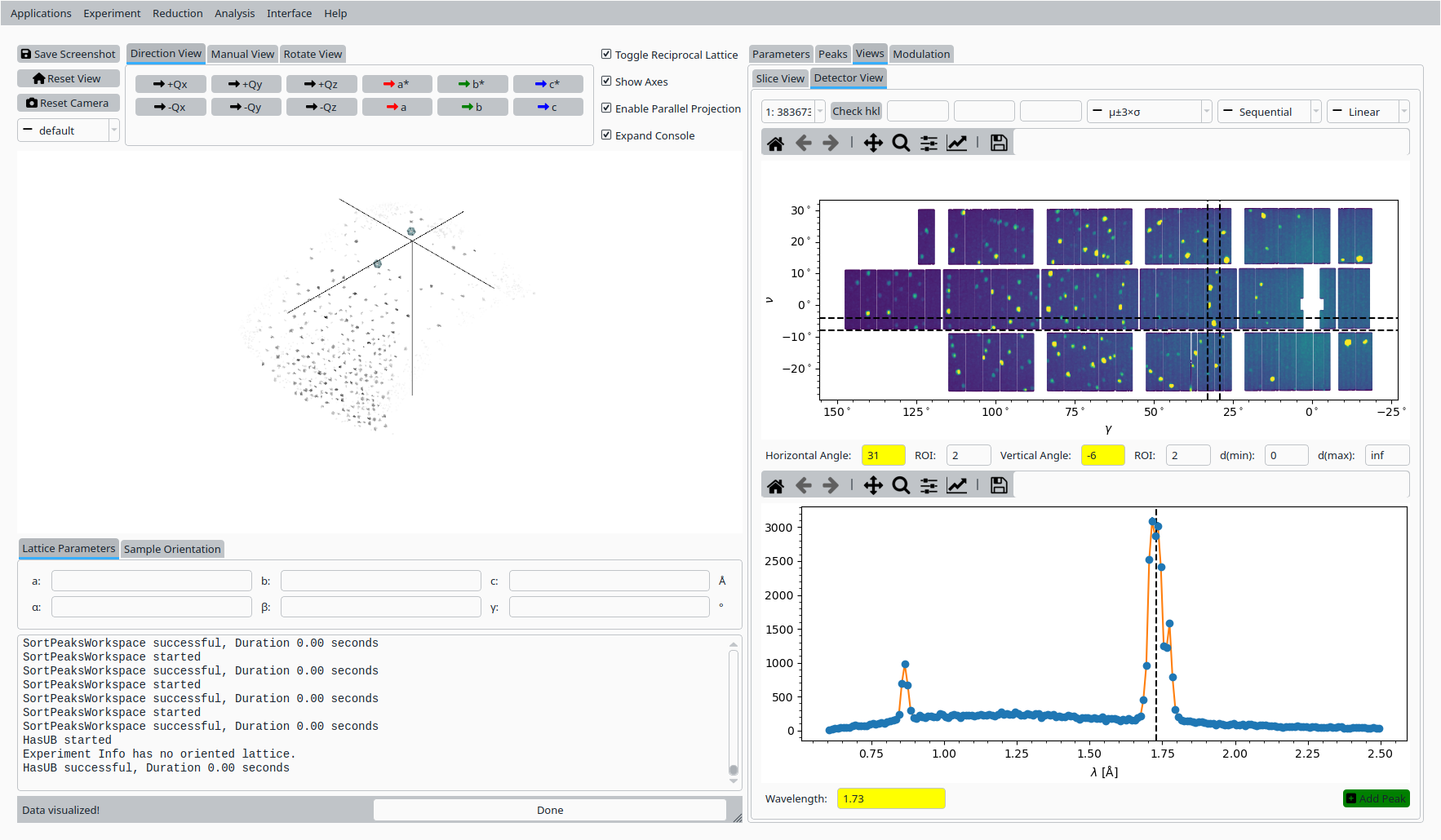
Second reference peak for Natrolite on CORELLI.#
Step 3: Set initial UB from unit cell#
Back in the UB tools interface:
Enter approximate lattice parameters for Natrolite (a, b, c and angles \(\alpha\), \(\beta\), \(\gamma\)).
Click Set UB to construct an initial UB matrix from these lattice parameters and the reference peaks.
Initial UB matrix based on the Natrolite unit cell.#
Step 4: Hand index reference peaks#
In the Peaks tab:
Select the first reference peak in the table.
Enter its expected (h, k, l) values in the hand-indexing fields.
Use the helper controls to copy the integer indices and calculate the predicted peak position.
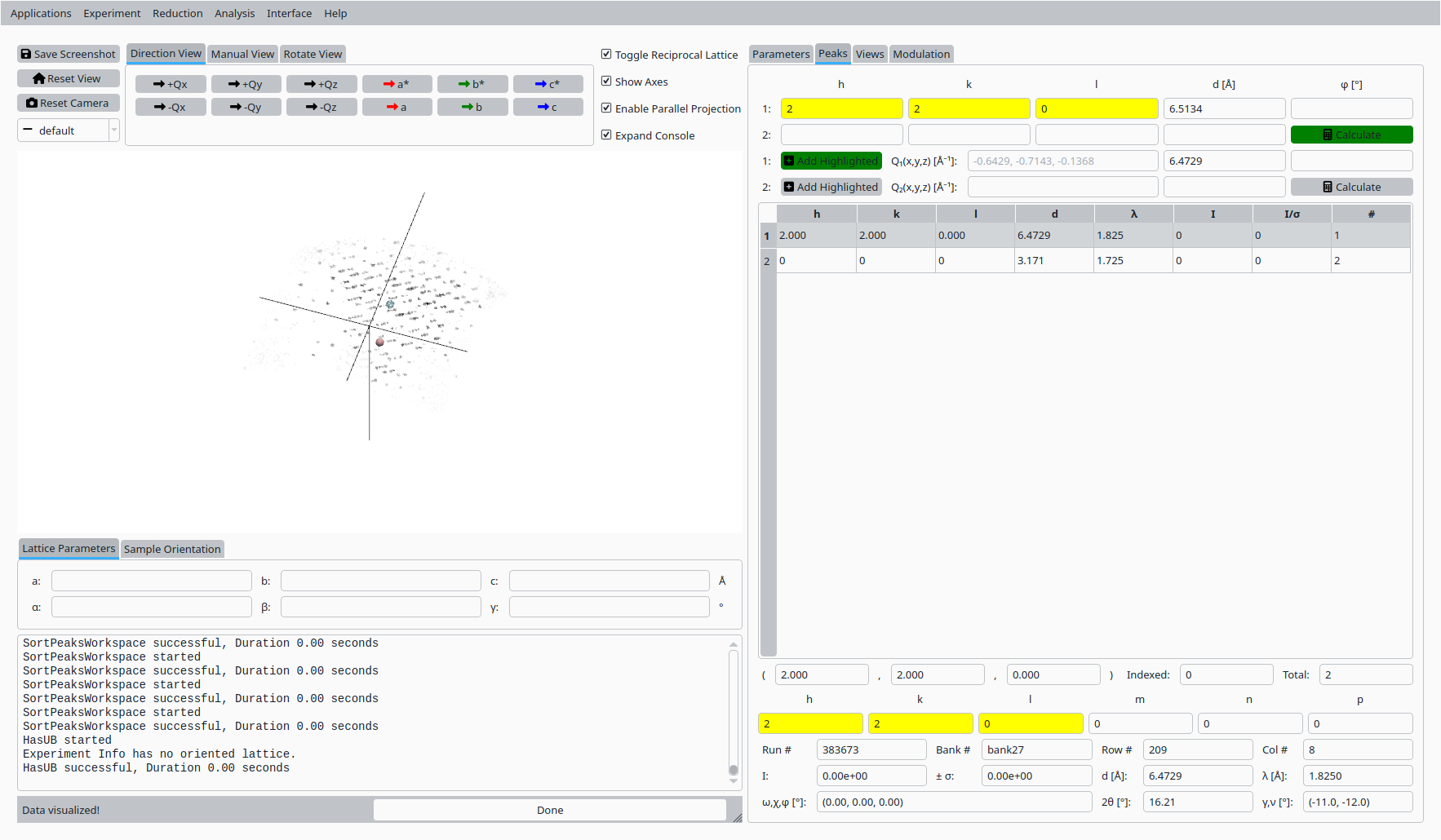
Hand indexing the first Natrolite peak.#
Select the second reference peak and repeat the hand-indexing procedure for its (h, k, l) values.
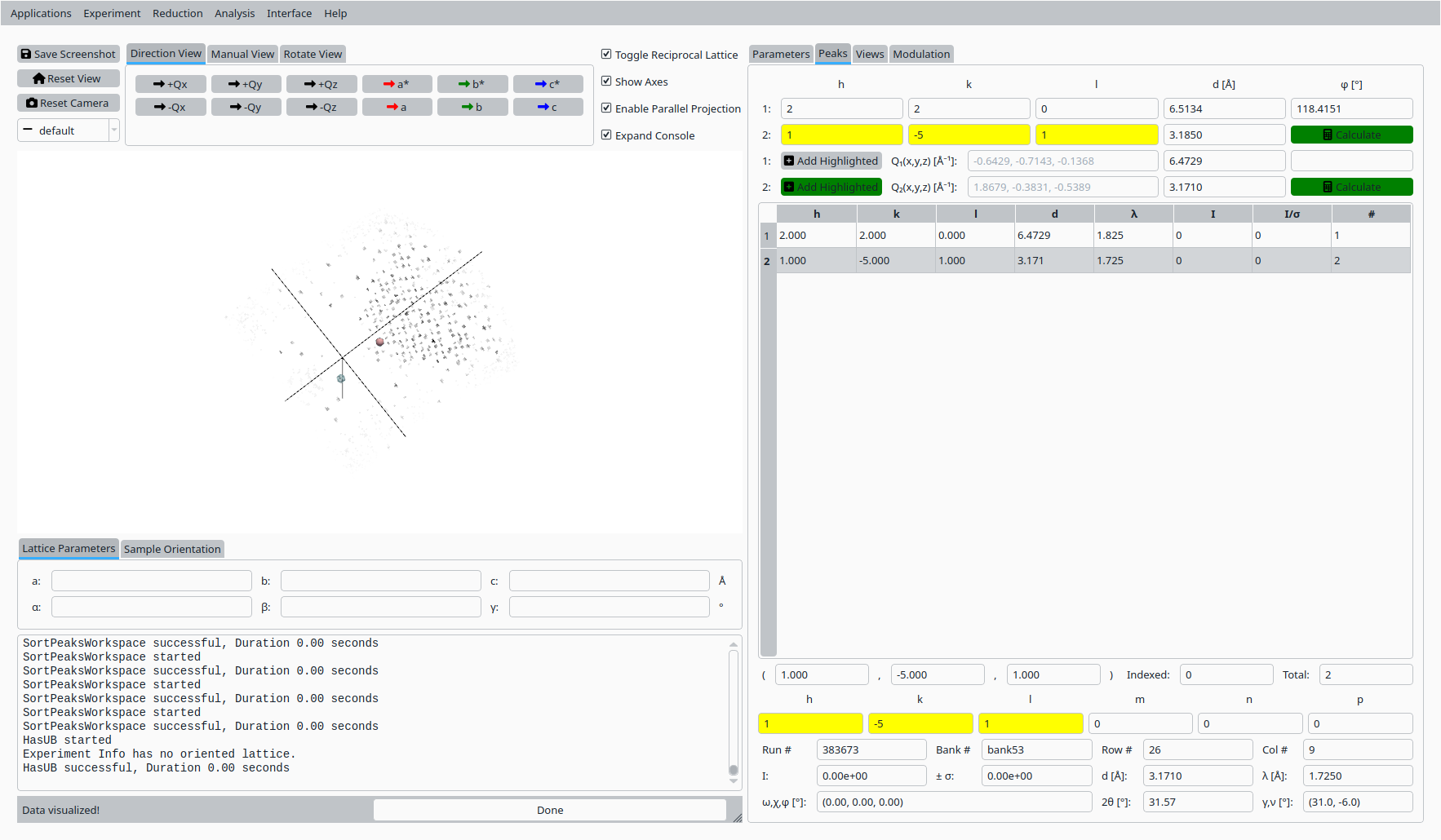
Hand indexing the second Natrolite peak.#
Step 5: Refine UB matrix (constrained)#
Back in the UB tab:
Choose an optimization mode such as Constrained that reflects the expected symmetry.
Click Refine UB to refine the UB matrix using the indexed reference peaks.
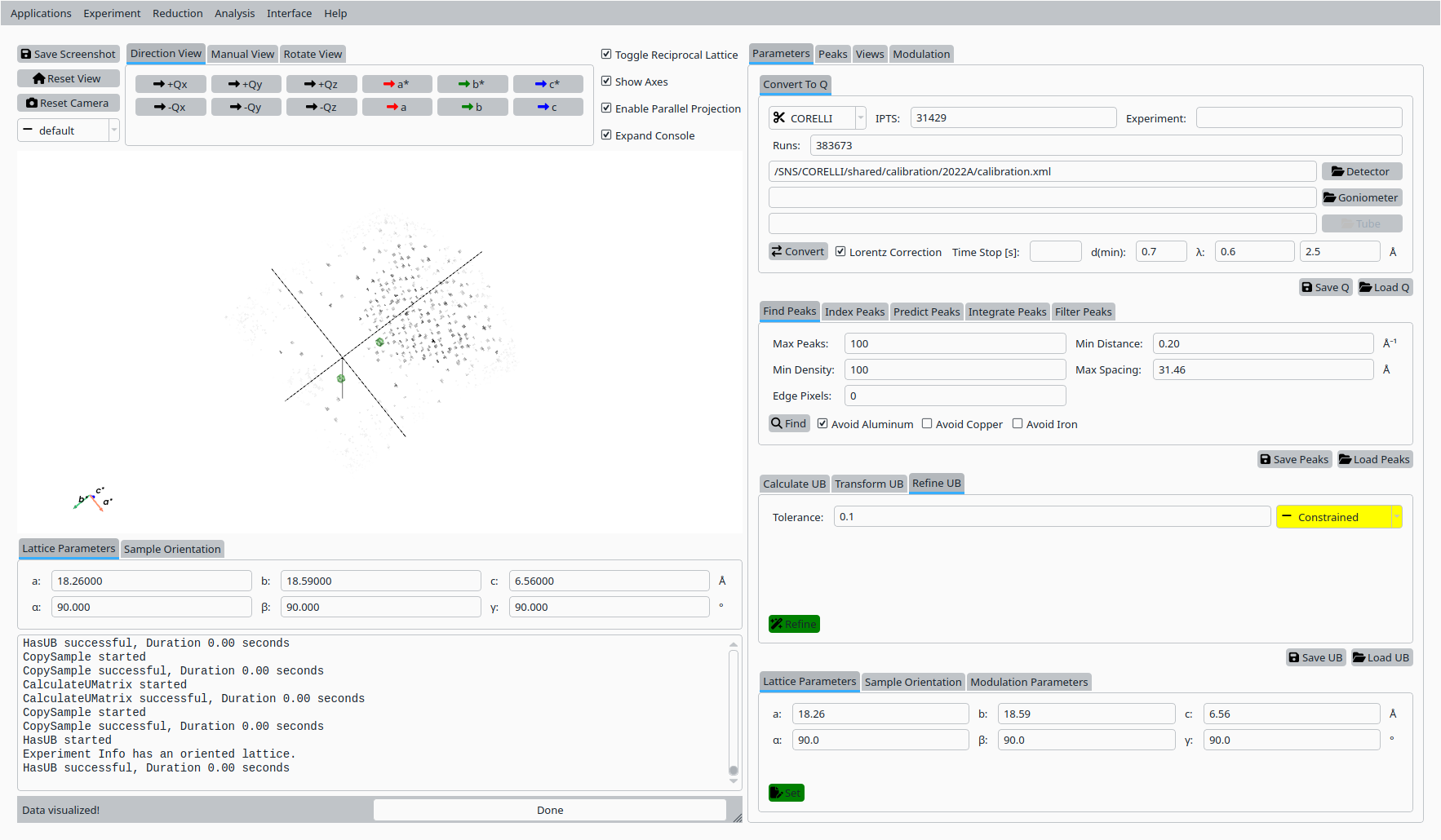
Refined UB matrix for Natrolite on CORELLI (constrained).#
Step 6: Index peaks#
In the Peaks tab:
Switch to the indexing sub-tab if needed.
Click Index Peaks to apply the refined UB matrix to the peak list and assign Miller indices.
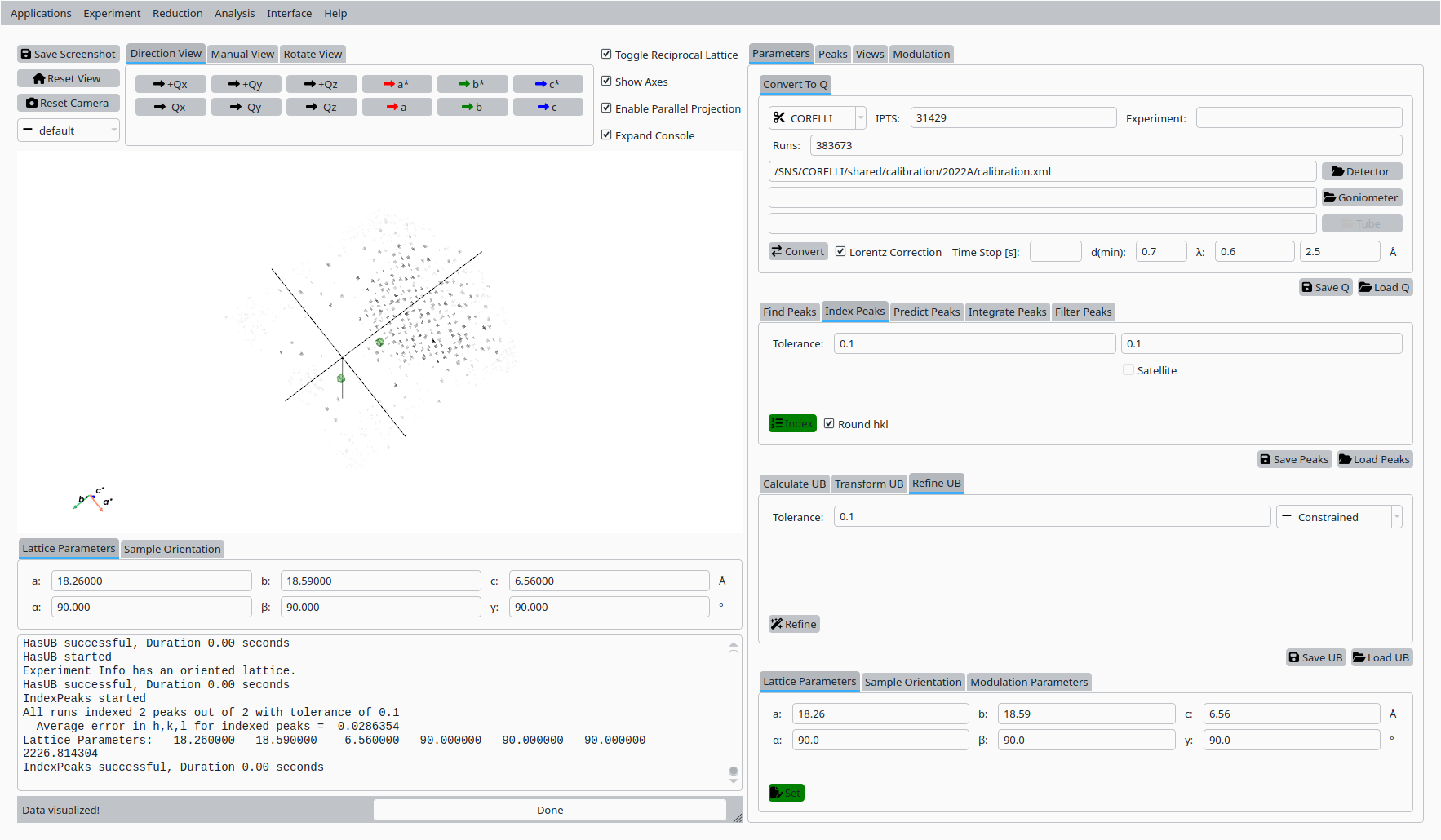
Automatic indexing of Natrolite peaks.#
Step 7: Predict, integrate, and filter peaks#
In the Analyze Peaks workflow:
Use the Predict Peaks controls to propose additional peaks based on the current UB matrix and centering.
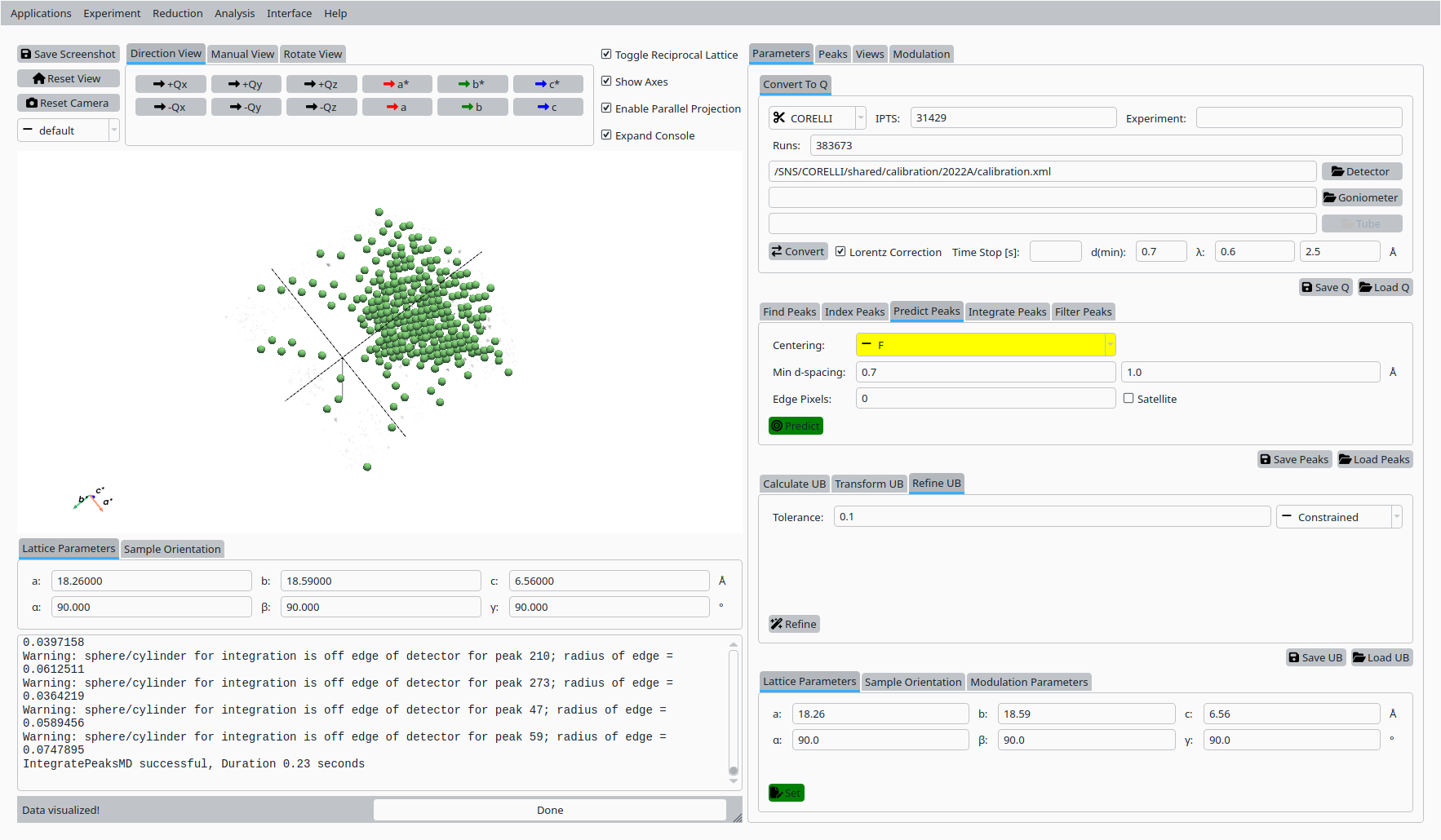
Predicted Natrolite peaks based on the refined UB.#
Enable adaptive and centroid options as needed and click Integrate Peaks to integrate the predicted peaks.
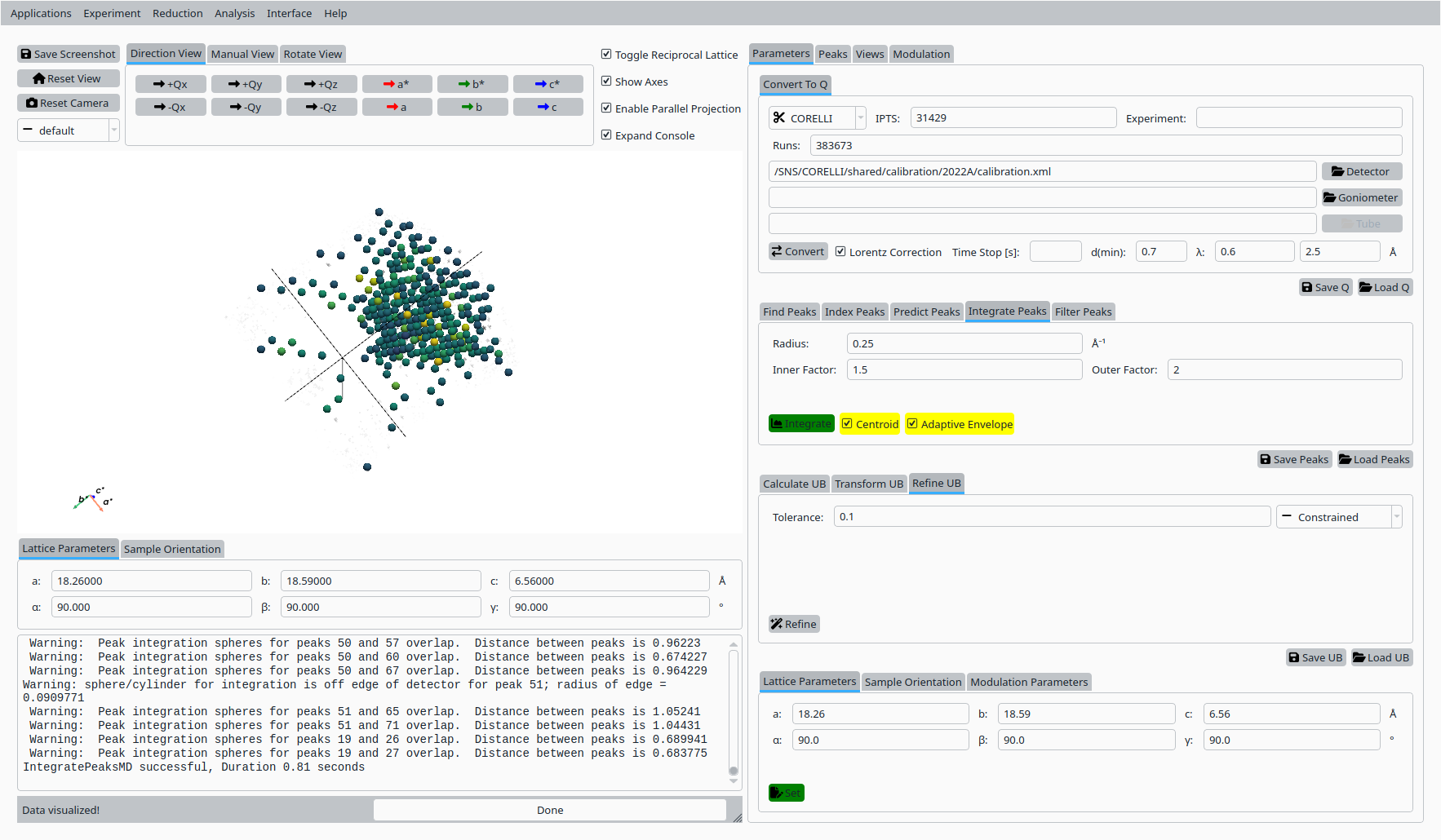
Integrated Natrolite peaks.#
Apply a filter on peak intensity or signal-to-noise using the Filter Peaks controls to refine the working peak list.
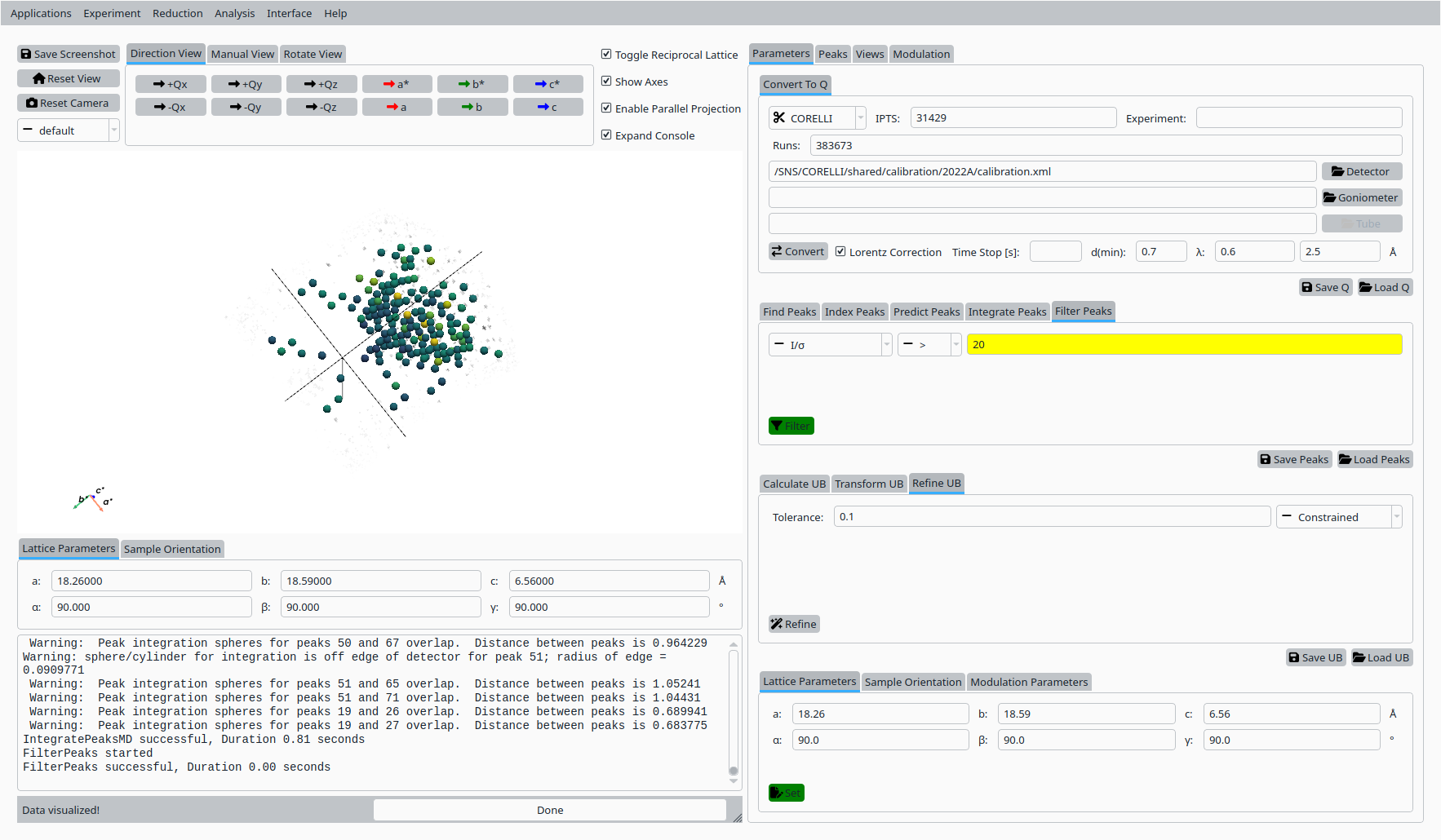
Filtered Natrolite peak list.#
Step 8: Refine UB matrix (orthorhombic)#
Return to the UB tab:
Change the optimization mode to Orthorhombic (or another appropriate symmetry).
Click Refine UB again to update the UB matrix using the filtered, integrated peaks.
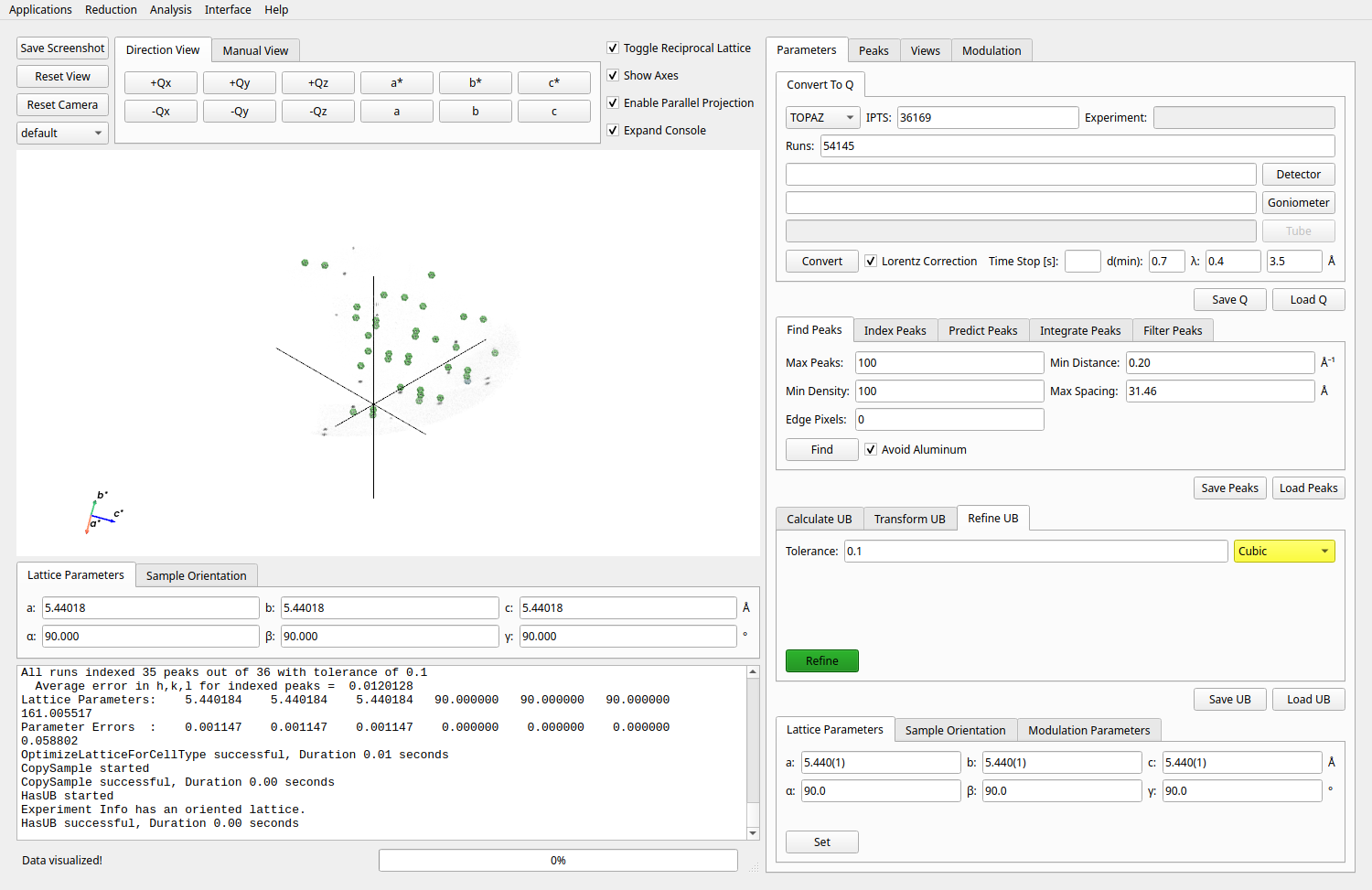
Final UB refinement for Natrolite on CORELLI.#
Step 9: View indexed peaks#
In the Peaks tab:
Select a peak from the table to highlight it in the Q-space view.
Inspect the indexing, Q position, and fit quality for the selected reflection.
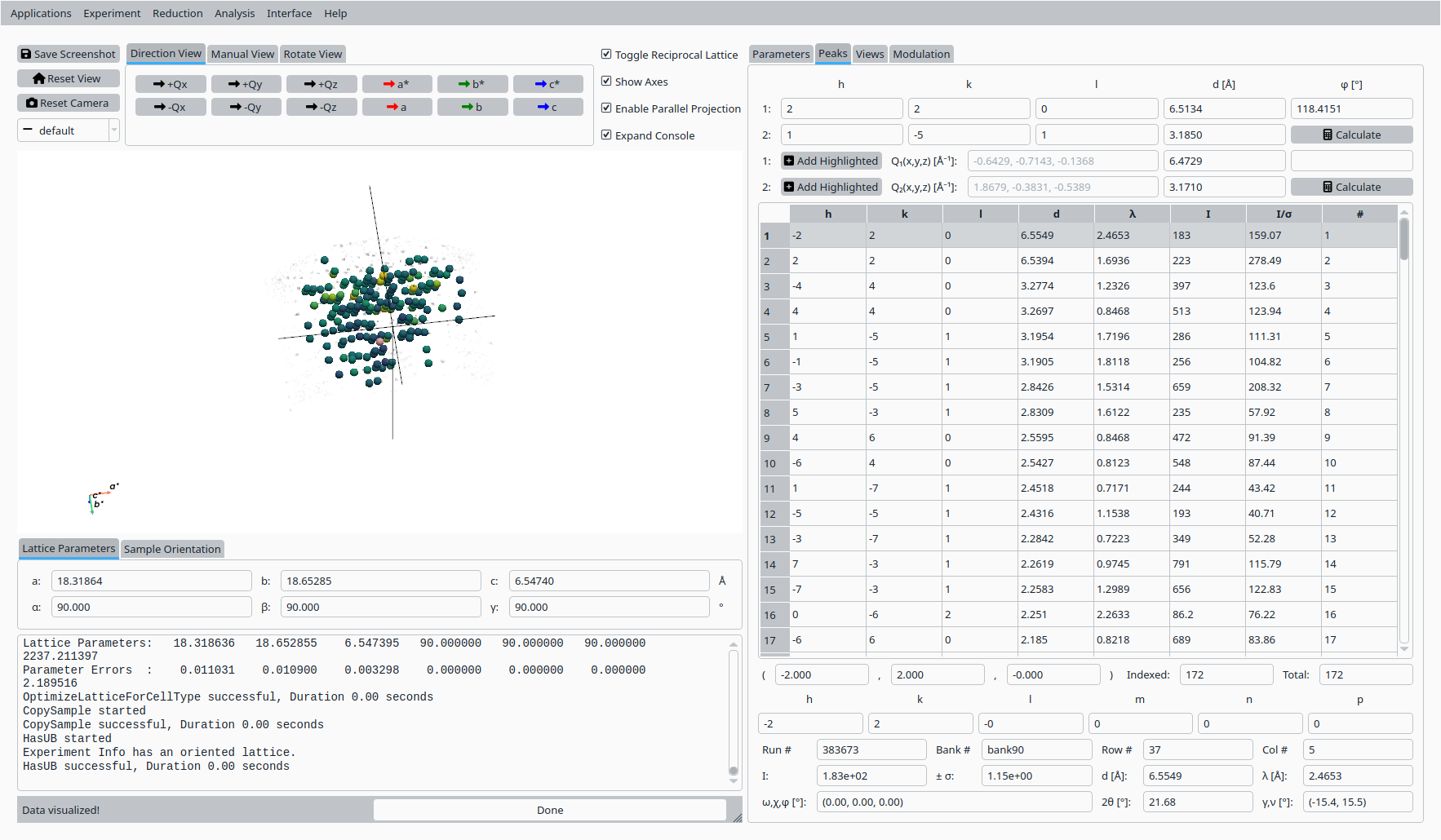
View and inspect an indexed Natrolite peak.#
Step 10: Slice view#
In the Convert to HKL tab:
Choose a slice direction and coordinate.
Click Convert to HKL to generate a reciprocal-space slice based on the refined UB matrix.
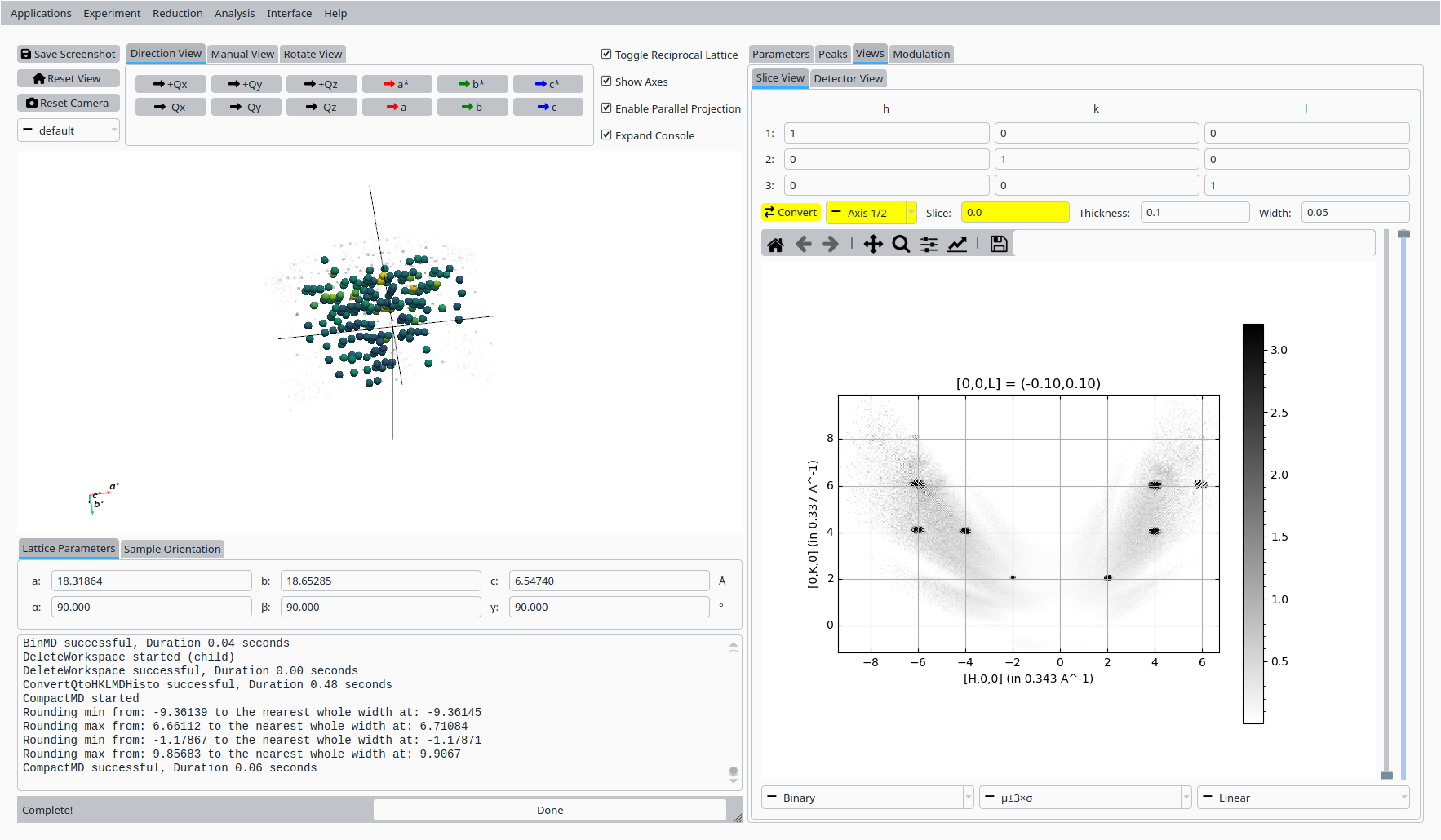
HKL slice view for the refined Natrolite UB.#
Step 11: Save UB#
Back in the Convert to Q tab:
Click Save UB to write the refined UB matrix to disk for use in subsequent CORELLI Natrolite analysis.
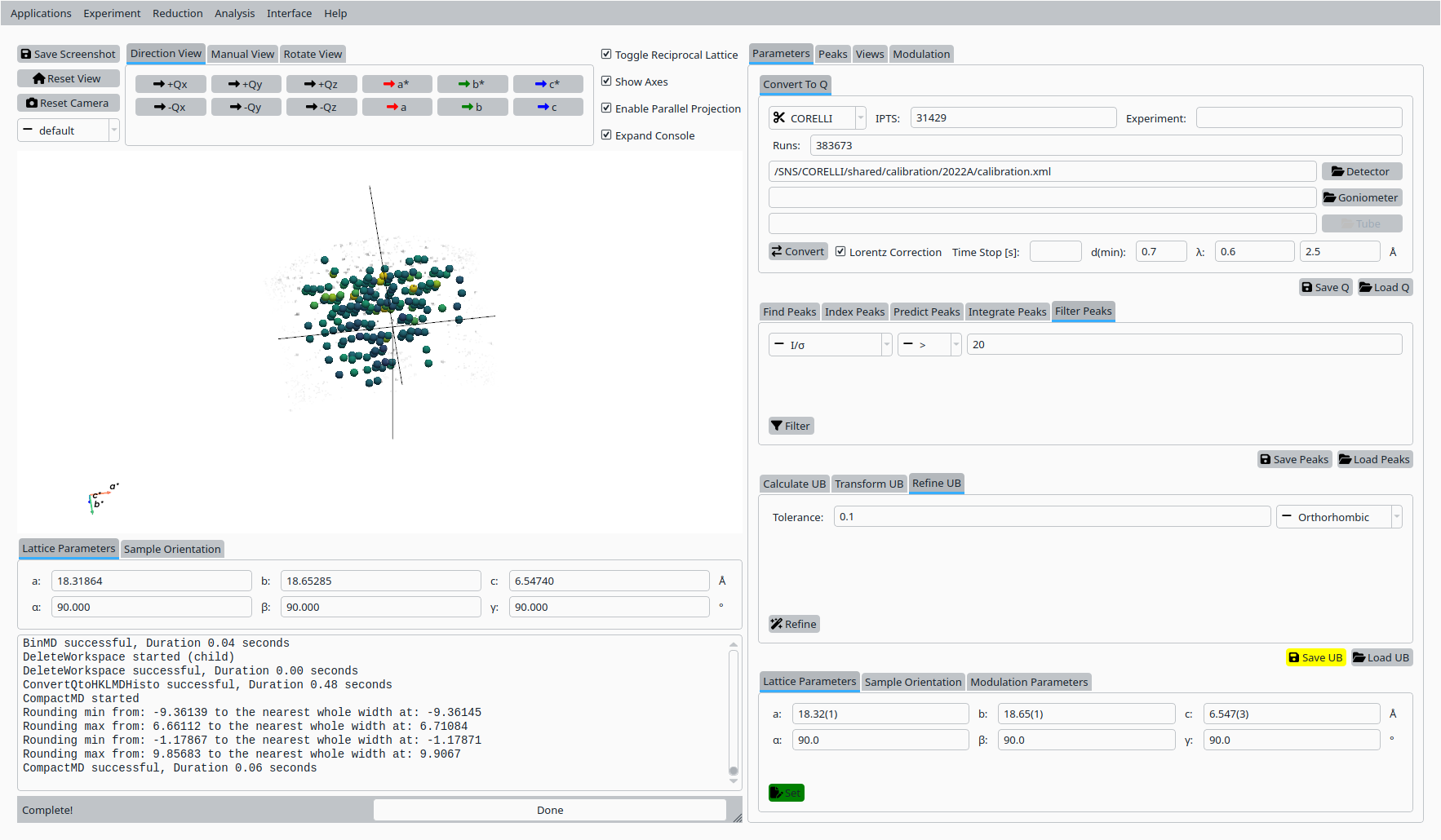
Save the refined UB matrix for Natrolite.#