UB Tools with Scolecite Data#
This tutorial demonstrates how to use the UB tools in NeuXtalViz to process TOPAZ Scolecite data (chemical formula \(\mathrm{CaAl_2Si_3O_{10}\cdot 3H_2O}\)).
Step 1: Convert to Q#
In the Convert to Q tab:
Select the TOPAZ instrument.
Enter the IPTS and run numbers for the Scolecite dataset.
(Optionally) set wavelength and calibration options as needed.
Click Convert to Q to load the data and build the Q volume.
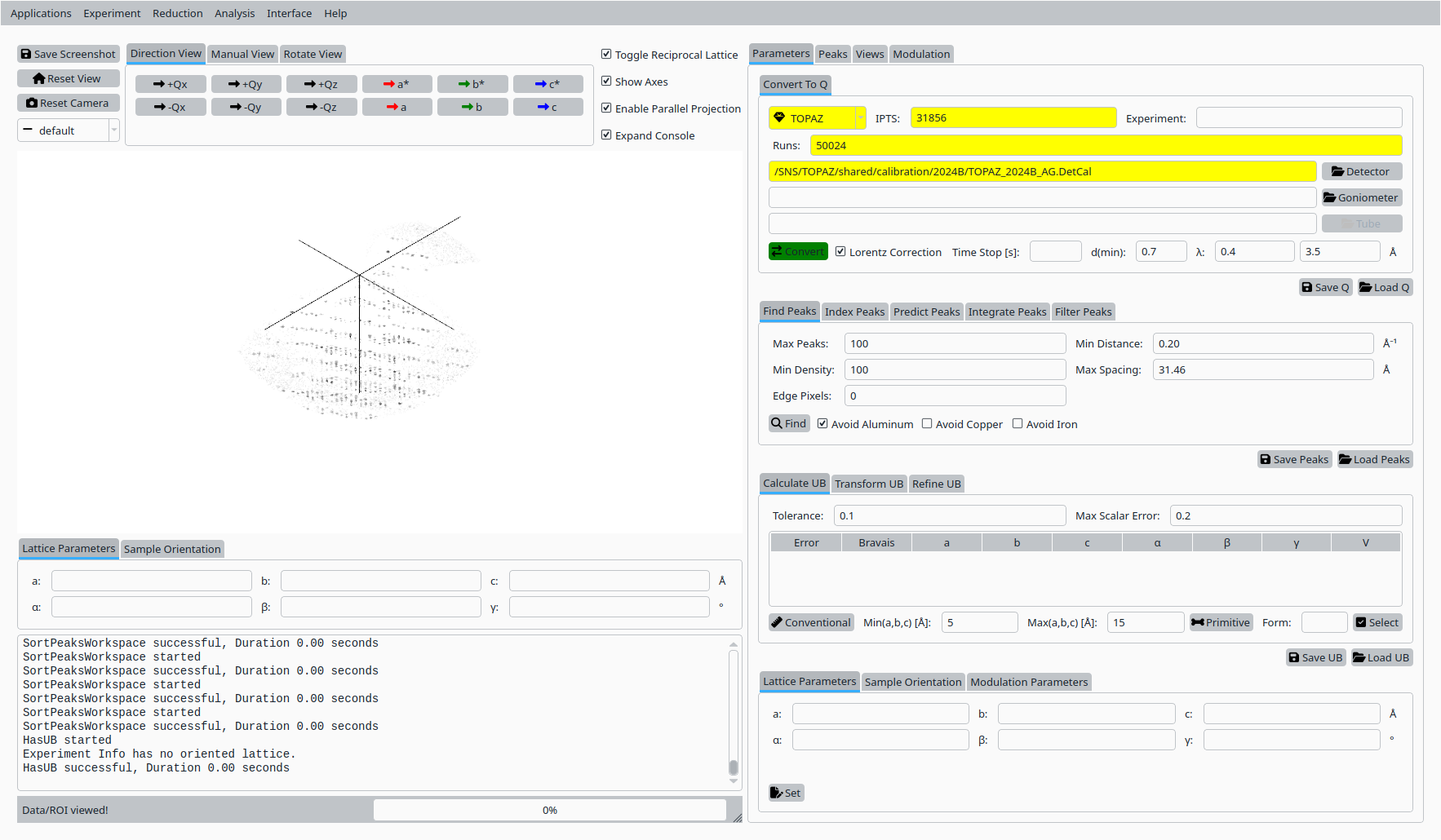
Convert Scolecite data to Q for TOPAZ.#
Step 2: Find peaks#
Still in the Convert to Q tab:
Adjust the peak-finding parameters (maximum number of peaks, density threshold, minimum distance).
Click Find Peaks to locate Bragg peaks in the Q volume.
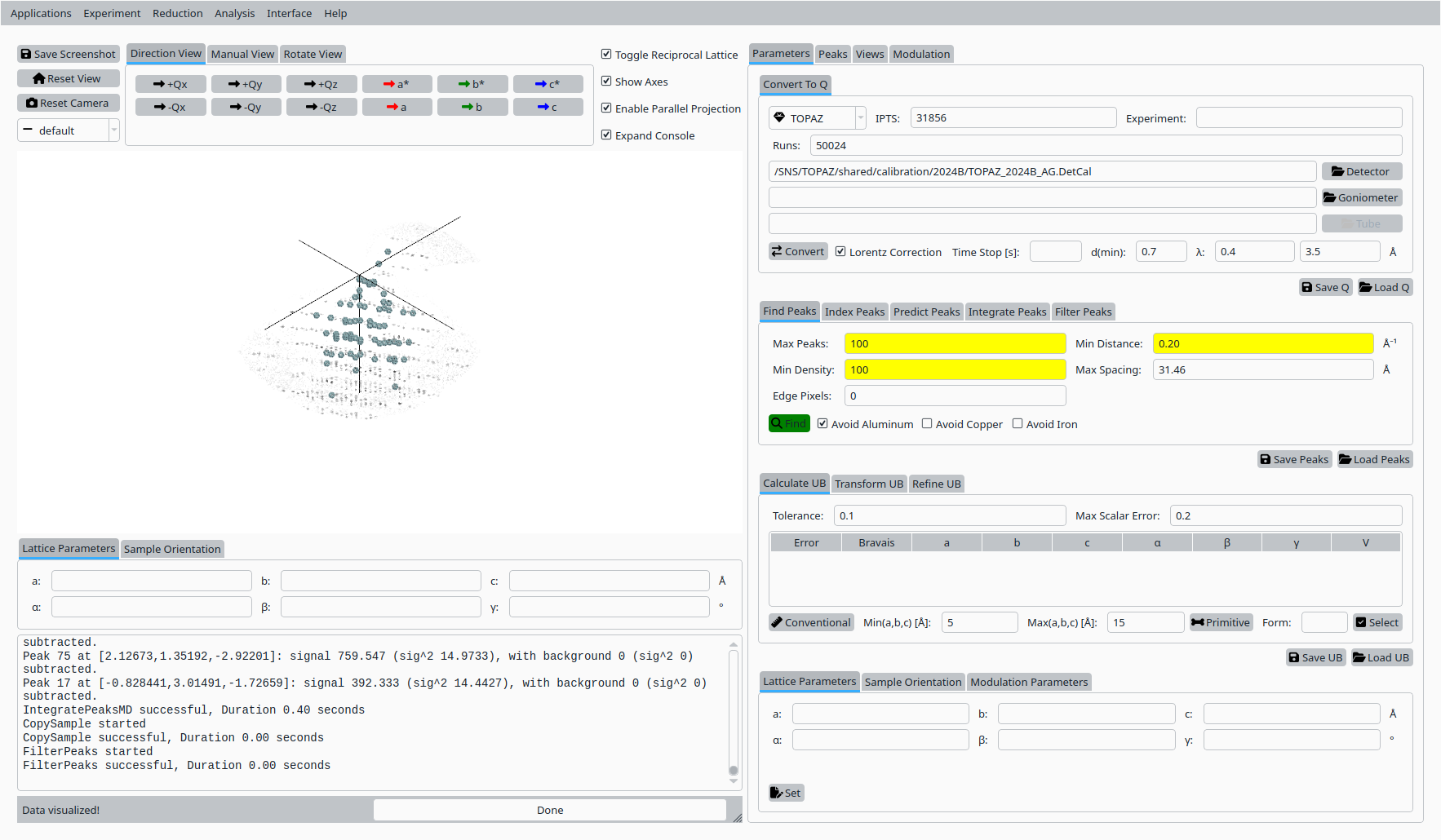
Find Bragg peaks in the Scolecite Q volume.#
Step 3: Primitive cell#
In the UB tab:
Set tolerances and cell-parameter bounds for the Niggli reduction.
Click Primitive Cell (Niggli) to search for a primitive cell consistent with the peak list.
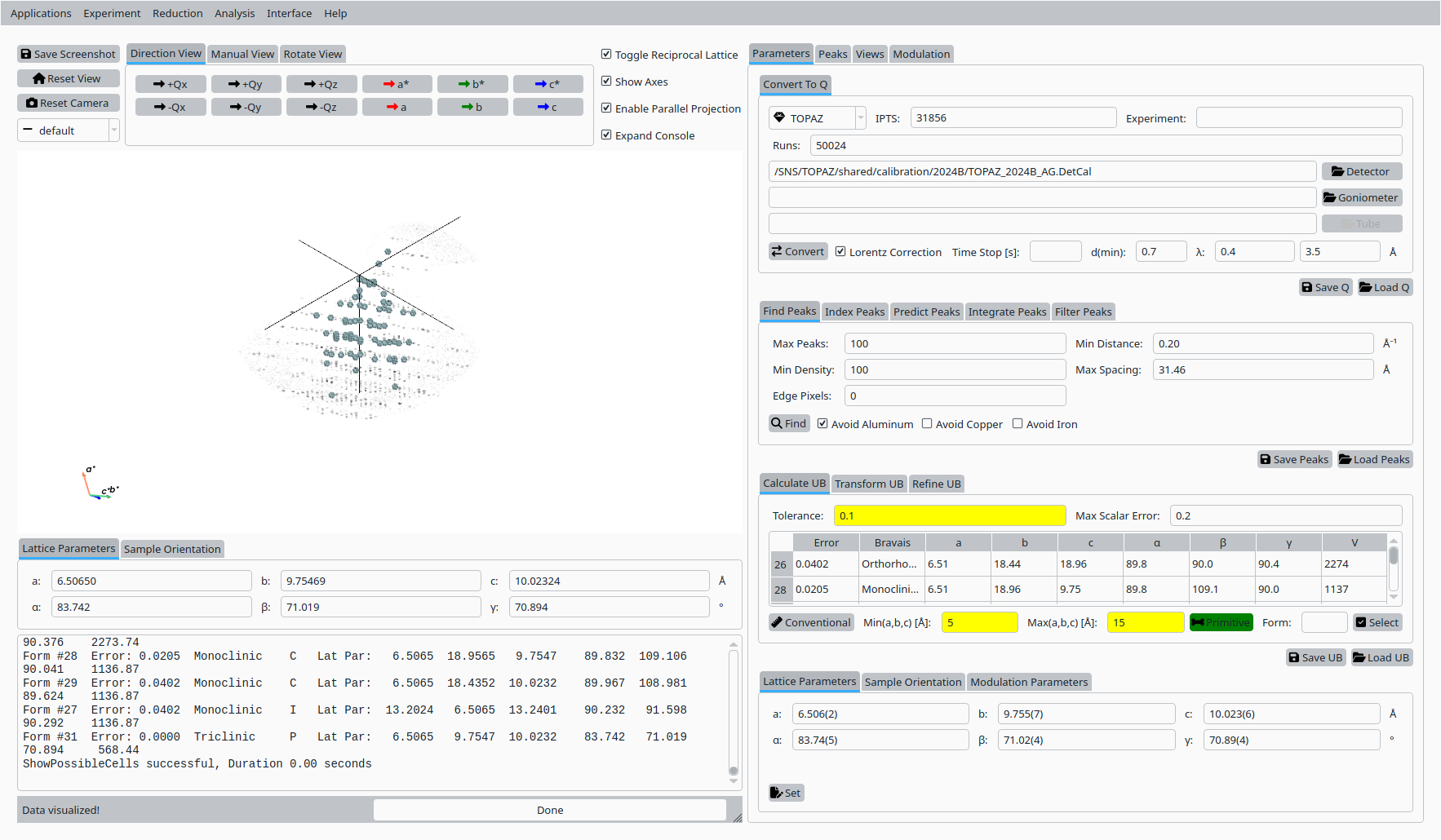
Primitive cell solutions for Scolecite.#
Step 4: Conventional cell#
From the list of candidate cells:
Select the row corresponding to the desired conventional cell.
Click Select to adopt it as the working unit cell.
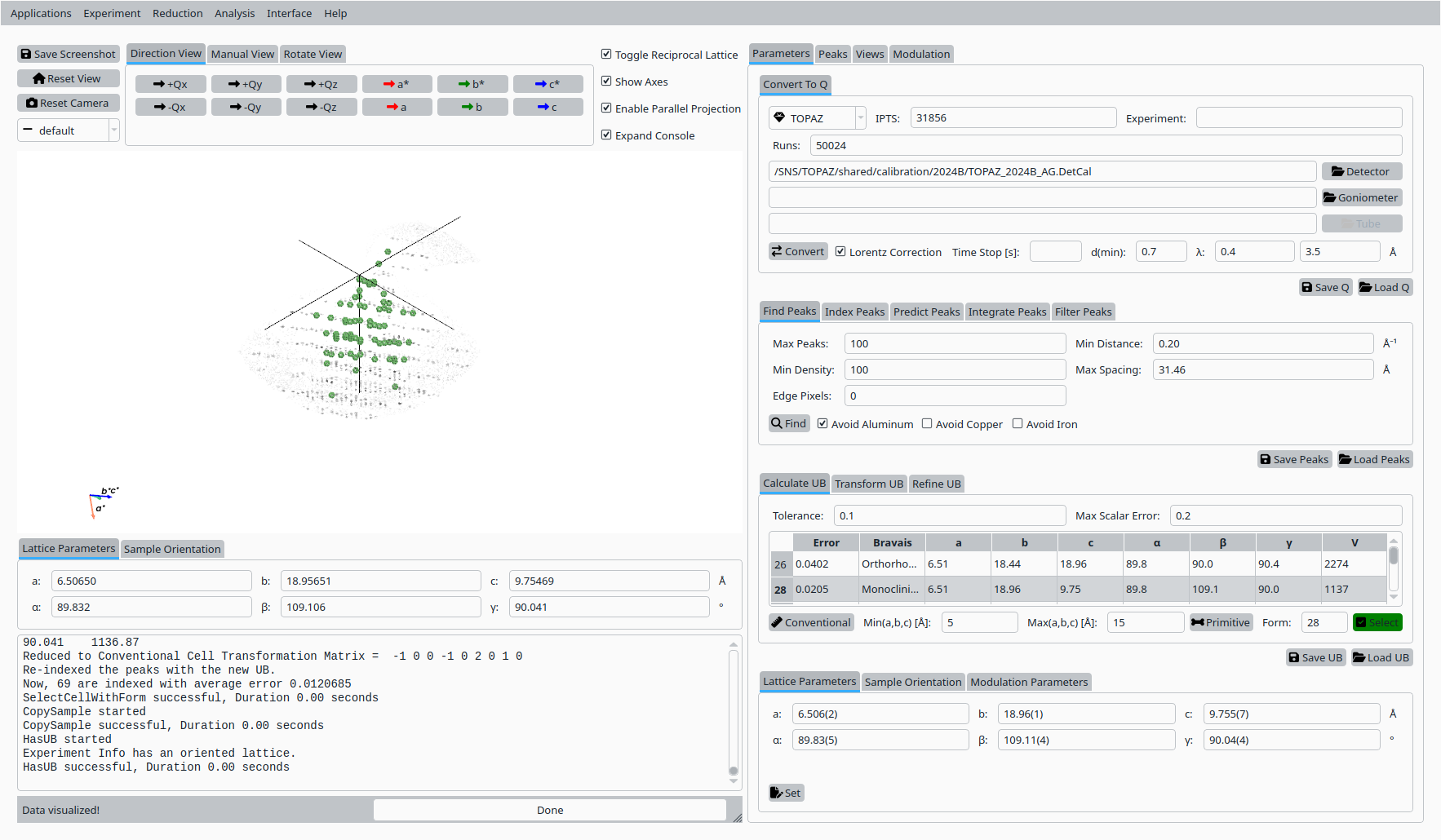
Select a conventional cell for Scolecite on TOPAZ.#
Step 5: Refine UB matrix#
With the conventional cell selected:
Choose an optimization mode (for example, Monoclinic).
Click Refine UB to refine the UB matrix against the peak list.
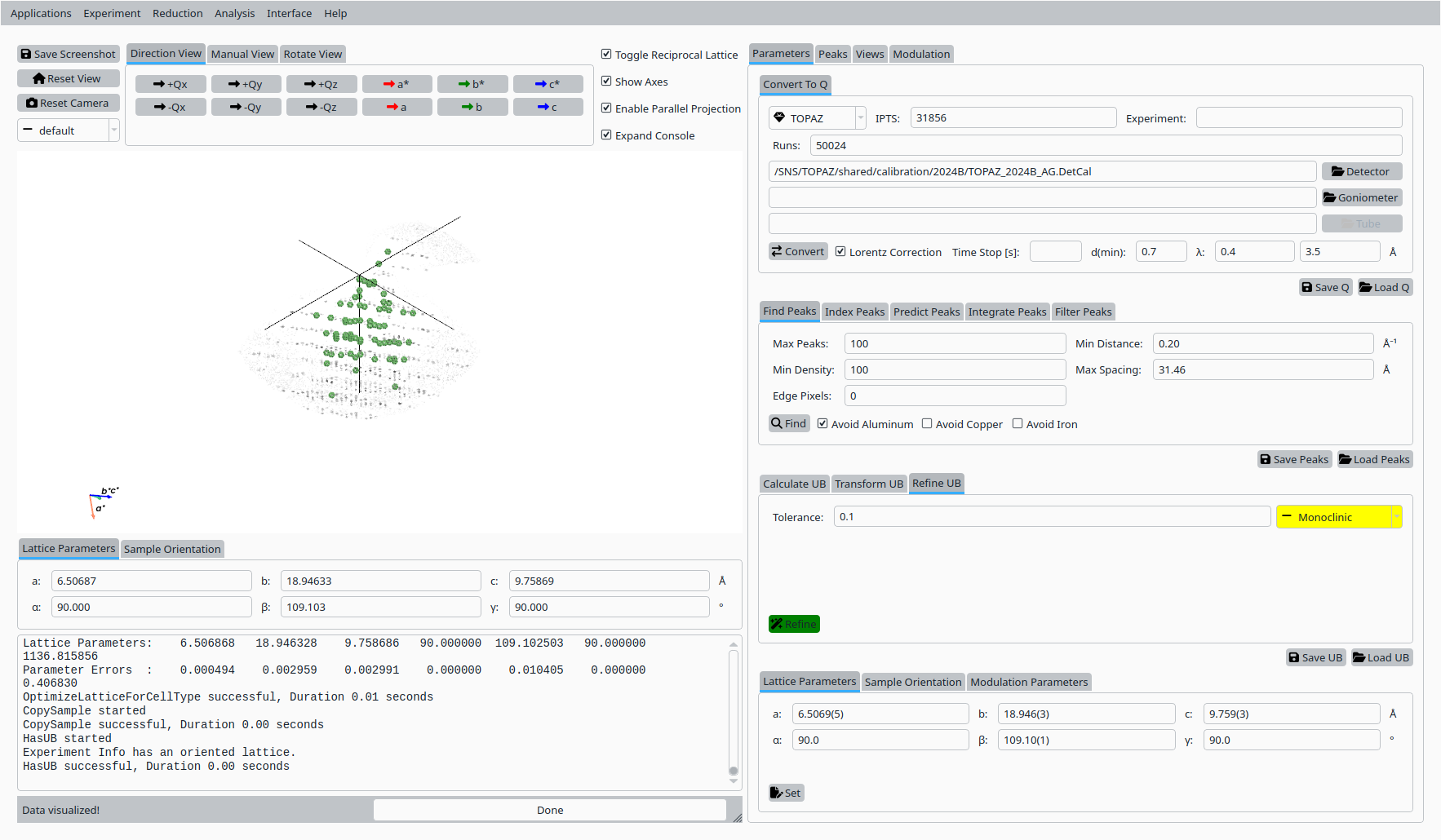
Refined UB matrix for Scolecite.#
Step 6: View indexed peaks#
In the Peaks tab:
Select a peak in the table to highlight it in the Q-space view.
Inspect the indexing and fit quality.
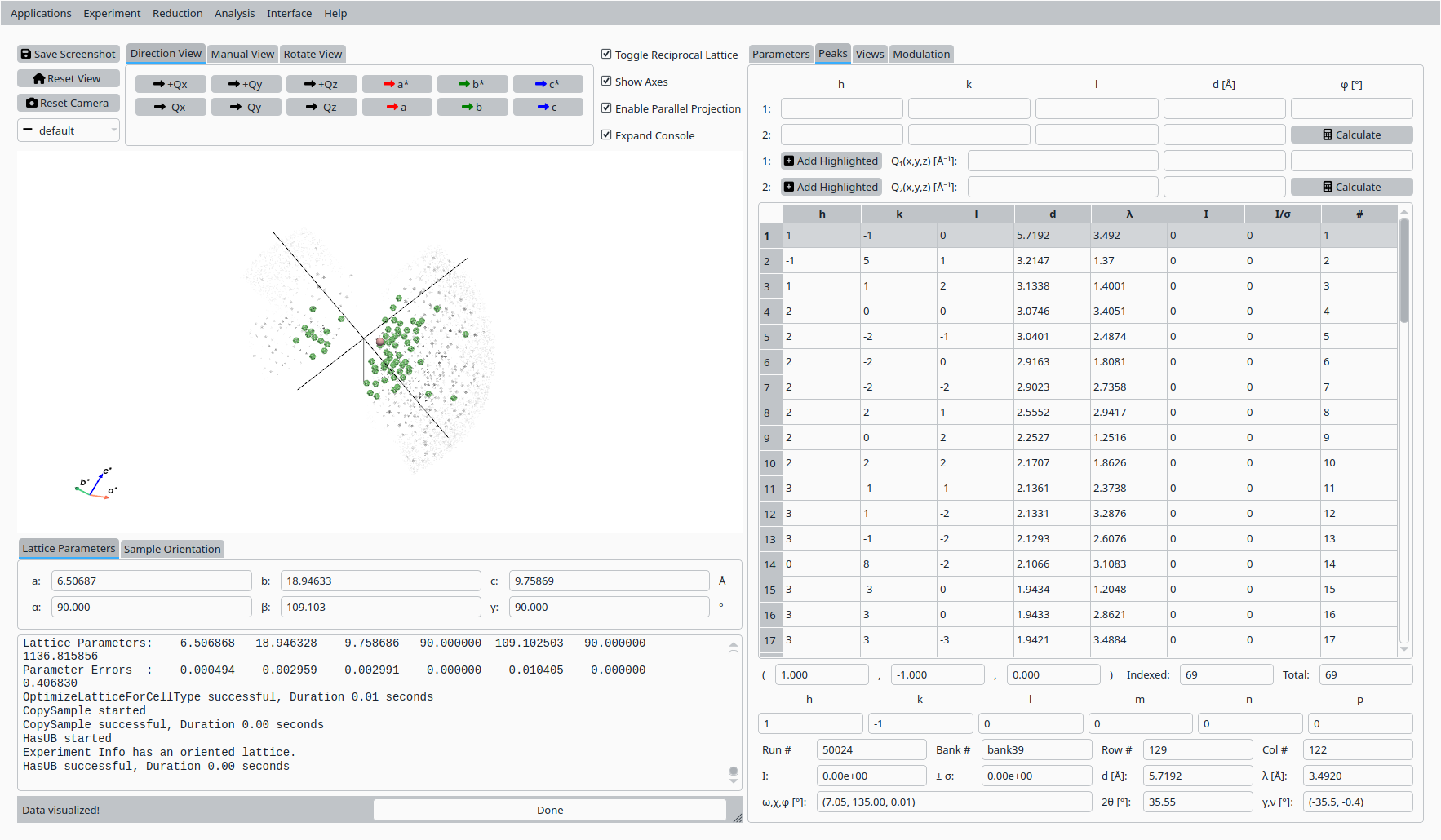
View and inspect an indexed peak.#
Step 7: HKL slice view#
In the Convert to HKL tab:
Choose a slice direction and coordinate.
Click Convert to HKL to generate a reciprocal-space slice.
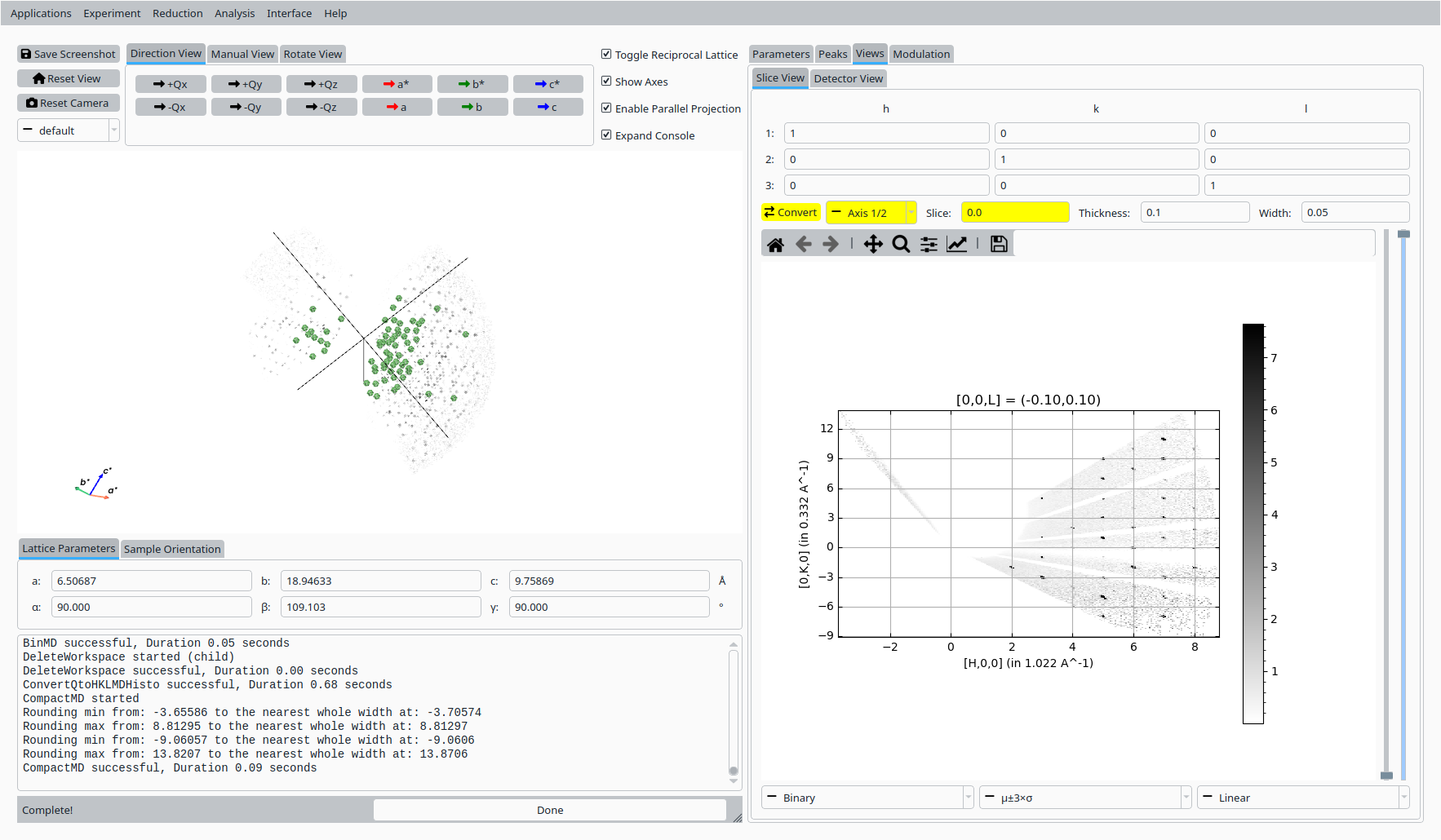
HKL slice view for the refined UB.#
Step 8: Save UB#
Back in the Convert to Q tab:
Click Save UB to write the refined UB matrix to disk for use in subsequent analysis.
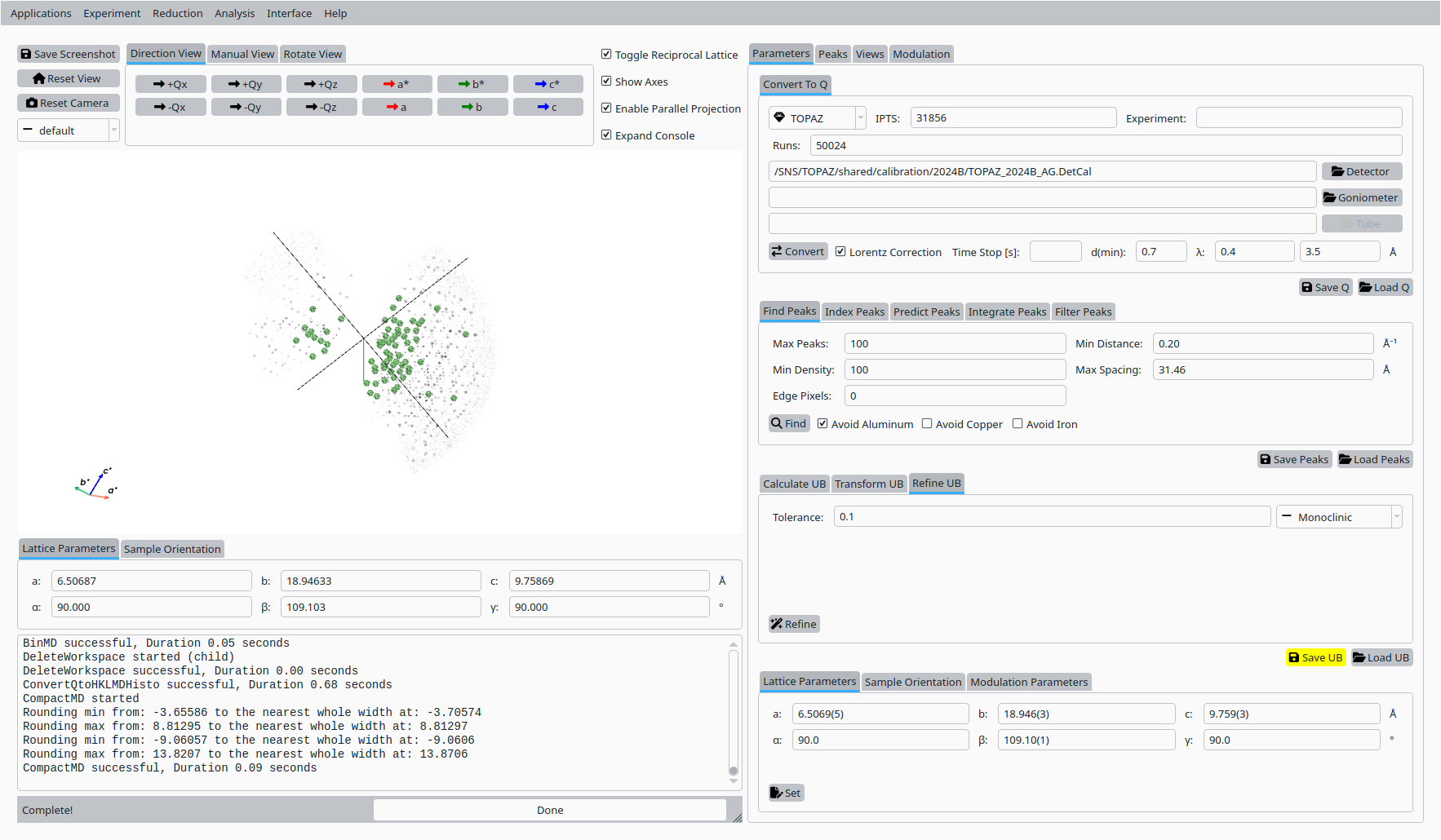
Save the refined UB matrix for Scolecite.#